How can I check if my router or computer is capable of high Internet speeds?
 Updated
by FibreStream
Updated
by FibreStream
Wireless routers
For packages that provide speeds above 100 Mbps, you will need a gigabit router. Gigabit means that the router can attain and distribute speeds up to 1000 Mbps (gigabit).
Router manufacturers typically include the word gigabit in their marketing, router names and descriptions. Non-gigabit routers will not include gigabit. The TP-Link Archer C7, for example, is a gigabit router:

A gigabit router has an internal network card capable of receiving speeds up to 1000 Mbps.
Router manufacturers often advertise wireless speeds over 100 Mbps when in reality, the router isn't capable of broadcasting those speeds because its internal network card isn't designed to receive more than 100 Mbps. For example, a router like the TP-Link Archer C20 is not gigabit, but TP-Link will market speeds above 100 Mbps:

The 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz speeds included in the title (in this case, 300mbps and 433mbps) are only attainable theoretically.
If the router had an internal network card capable of receiving higher speeds (gigabit), this router could distribute those speeds wirelessly. But since it does not have a gigabit network card, it cannot distribute the marketed speeds.
To ensure your router is gigabit, verify the router model by visiting the manufacturer website. If the router is gigabit capable, it'll be noted in the router name or description.
Computers
The capability of your internal network card can be determined in the operating system.
Windows (7 and 10)
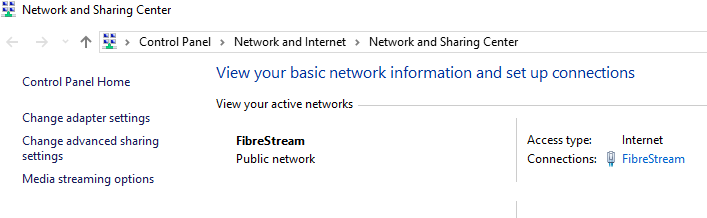
- Navigate to Network and Sharing Centre.
- Select Change adapter settings.
- Right click on the Internet connection/adapter in use.
 There may be several Internet connections listed in Network Connections. Most of them will likely include a red X. That indicates that the connection is disabled, offline, or not in use.
There may be several Internet connections listed in Network Connections. Most of them will likely include a red X. That indicates that the connection is disabled, offline, or not in use.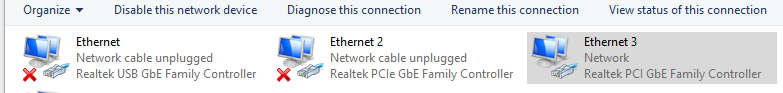
- Select Properties.
- Select Configure.
- Select the Advanced tab.
- Select Speed & Duplex.
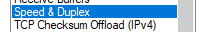
- The Value menu will list all available negotiation speeds.
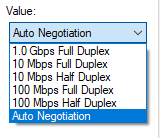
If 1.0 Gbps is listed, the network card is gigabit compatible. If 1.0 Gbps is not listed, the card is not gigabit compatible.
macOS
- Click the Apple menu and select System Preferences.
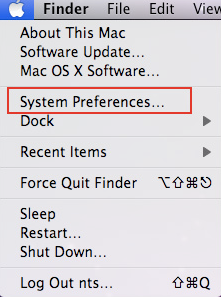
- In the Internet & Network section, double-click the Network icon.
- Select Ethernet from the left-hand menu.
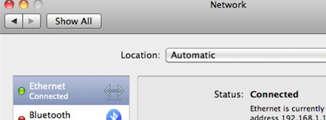
- Select the Advanced button.
- Select the Ethernet tab.
- Change Configure to "Manually" and select the speed drop down. If 1000baseT is available, your network card is gigabit compatible. If 1000baseT is not listed, it is not gigabit compatible.
